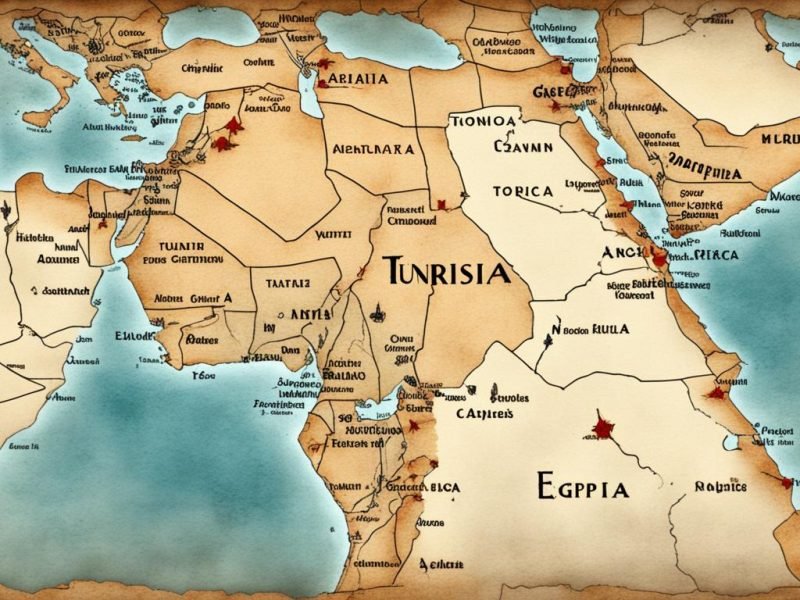
Did you know that only 37% of people surveyed knew where Tunisia is on a map? Many folks think Tunisia is in Egypt. But, Tunisia and Egypt are different, even though they’re in North Africa.
Tunisia and Egypt are their own countries. They have their lines on the map, leaders, and ways of life. Although Egypt is near, Tunisia and Egypt are unique places. They’re not the same, but they work together in groups like the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation, Arab League, and the United Nations.
Key Takeaways
- Tunisia and Egypt are separate sovereign states in North Africa.
- Despite their proximity, Tunisia is not part of Egypt.
- Tunisia location is bordered by Algeria and Libya, while Egypt neighbours Libya, Sudan, Israel, and Gaza Strip.
- The two countries share cultural and regional affiliations but maintain their distinct identities.
- They are members of international organisations like the Arab League and the African Union.
Understanding the Geography of North Africa
North Africa’s landscape is varied and very interesting. It includes different types of land and a long history. This area is made up of several countries. Each one is special and adds to North Africa’s overall character.
Location of Tunisia
Tunisia is at the top of Africa. It has Algeria on the west and Libya on the east. The Mediterranean Sea is to its north and east. Being in this spot has helped Tunisia mix with other countries in North Africa and Europe.
Location of Egypt
Egypt is also in a key spot in North Africa. It’s northeast of Tunisia. The Mediterranean Sea is to its north and the Red Sea to its east. Egypt’s land and history are very important to the area.
North African Countries
North Africa includes Tunisia, Egypt, Morocco, Algeria, and Libya. They are often called the ‘Maghreb’. These countries are linked by history, culture, and politics. They show how different yet connected North African nations are.
| Country | Capital | Neighbouring Countries |
|---|---|---|
| Tunisia | Tunis | Algeria, Libya |
| Egypt | Cairo | Libya, Sudan, Israel, Gaza Strip |
| Morocco | Algeria | |
| Algeria | Algiers | Tunisia, Morocco, Libya, Mali, Niger, Mauritania |
| Libya | Tripoli | Egypt, Tunisia, Algeria, Chad, Niger |
The Borders of Egypt
Egypt sits in a unique spot that makes it very important. To the north, it meets the Mediterranean Sea. This sea is a key route for ships connecting to other waters.
The Red Sea is on its eastern side. It’s important for trading on water. On the west, there’s Libya, and Sudan is to the south. These neighbours highlight Egypt’s key role in North Africa.
To the northeast, Egypt is next to the Gaza Strip and Israel. This underlines Egypt’s big role not just in Africa but the Middle East too. These borders help shape Egypt’s safety measures and trade rules. This boosts its importance on the continent.
Here is a detailed table showcasing the various Egypt borders:
| Direction | Border | Significance |
|---|---|---|
| North | Mediterranean Sea | Maritime trade route, international waters |
| East | Red Sea | Trade and maritime activities |
| West | Libya | Regional cooperation, security |
| South | Sudan | Regional cooperation, security |
| Northeast | Gaza Strip, Israel | Geopolitical significance |
These Egypt borders mark the country’s edges and boost its power in the area. The seas are vital for global trade. The land borders are key for working together in the region and for safety.
The Historical Relations Between Egypt and Tunisia
Tunisia and Egypt have a long history together. Their story starts from ancient times and goes on till today. They have traded, shared culture and sometimes had conflicts. This has created a strong bond between them.
Antiquity to Medieval Relations
Long ago, Egypt and Carthage (ancient Tunisia) were big on trade and culture sharing. They traded a lot across the Mediterranean Sea. This brought them closer together. Both were influenced by the Greeks and Romans, sharing similar cultures and milestones.
Islam’s spread also brought Egypt and Tunisia closer. They were part of the same caliphate sometimes. They shared Islamic traditions and the Arabic language. Later, the Ottoman Empire included them both, making the ties stronger. This period made them quite similar in culture and governance.
Modern Relations and Connections
In recent times, Egypt and Tunisia have stayed connected. They were both colonised, Tunisia by France and Egypt by the British. Their fight for independence linked them to a bigger fight across Africa during the mid-20th century.
After gaining independence, they had both good and bad times. The Arab Spring was a big event for both but they reacted differently. Yet, they still work together in diplomacy and other areas. They often agree on issues about North Africa in international groups.
| Period | Key Aspect | Influence on Relations |
|---|---|---|
| Antiquity | Trade and Cultural Exchange | Strong economic ties |
| Arab Caliphates | Islamic Spread | Cultural and religious unity |
| Ottoman Empire | Administrative Similarities | Enhanced political coherence |
| Modern Era | Colonisation and Independence | Fluctuating diplomatic relations |
| Post-Arab Spring | Political and Economic Cooperation | Renewed engagement |
The relationship between Tunisia and Egypt has evolved a lot. From ancient times to now, it has been strong. As they face new challenges, their past helps guide their future actions and goals together.
Is Tunisia Near Egypt?
Many people ask, “Is Tunisia near Egypt?” because they are curious. Tunisia and Egypt are in North Africa but not close to each other. Libya sits between them, making them far apart.

To see how far, look at their capitals, Tunis and Cairo. They are on opposite sides of North Africa. So, the answer to “Is Tunisia near Egypt?” is no.
| Tunis | Cairo | |
|---|---|---|
| Region | North Africa | North Africa |
| Distance from Each Other | Over 2,300 kilometres (around 1,450 miles) | |
| Intermediate Country | Libya | |
In North Africa, Tunisia and Egypt are quite far from each other. They are separated by Libya. So, they are not close neighbours at all.
The Cultural Ties Between Egypt and Tunisia
When we look at Egypt and Tunisia, we find deep connections. They share heritage and have always interacted. Their ties span language and religion, strengthened by cultural swaps.
Language and Religion
Arabic is vital in linking Egypt to Tunisia. It has grown over centuries with outside impacts. Even with local dialects, they understand each other. Islam guides both their cultures, influencing norms.
This religion shapes their traditions and daily life. It’s something they deeply share.
Significant Cultural Exchanges
Exchanges between the countries have built a common heritage. Old trade routes shared goods and ideas. Schools have worked together, sending students and scholars back and forth. This enriched both places.
Migrating over time also mixed their cultures. People moved, absorbing each other’s customs.
These shifts are seen in:
- Trade and Commerce: Crafts and food show their shared influences.
- Educational Collaborations: They’ve created joint study programs and exchanged scholars.
- Migration and Settlement: People moving have mixed their communities.
In short, Egypt and Tunisia are closely tied. Their connection comes from shared language and faith. History has woven their lives tightly together, enriching both cultures.
Exploring the Similarities and Differences
Egypt and Tunisia show us different things about their economy and trade and schools. It’s interesting to see what they do the same and what they do differently.
Economy and Trade
Both countries’ money comes a lot from farming and tourists. But, they grow in different ways. Tunisia works hard to do lots of different things. This helps women and kids have better rights and jobs. Egypt focuses on big building projects to make its economy stronger. So, the way they use their money and resources shows what’s important to them.
Education Systems
When we look at schools in Egypt and Tunisia, we see they teach kids in different ways. Tunisia teaches in French and Arabic, showing they like many languages. Egypt’s schools mostly teach in Arabic. But both places want their kids to learn lots and do well in the future. They have different classes to help kids get ready for different jobs.
- Economic Engagement – Agriculture and Tourism
- Developmental Strategies – Women’s Rights in Tunisia, Infrastructure in Egypt
- Education – Tunisian Bilingual System vs Egyptian Traditional Focus
Tourism in Egypt and Tunisia
North Africa tourism is special. It has both history and beauty. Egypt and Tunisia are top spots. Egypt destinations draw people with old monuments. Think of the Pyramids of Giza and the Sphinx. These places let you dive into Egypt’s rich past and ongoing story.
Tunisia wins hearts with its Mediterranean beauty. It has blue waters and old ruins like Carthage. Tunisia is filled with views and history. It mixes Arab and Mediterranean styles. This mix attracts lots of tourists.
North Africa tourism helps Egypt and Tunisia’s economies. In Egypt, tourism is key. It brings lots of tourists to see historical places and lively cities. Tunisia pulls in tourists with its lovely beaches and old sites.
Tunisia and Egypt cater to many interests. They offer archaeological sites and beaches. Their location in North Africa adds to their appeal. They share their unique attractions with tourists. This gives travellers a memorable mix of history and nature.
The Role of Both Nations in the African Union
Egypt and Tunisia are key members of the African Union. They work hard to bring together, keep peace, and grow sustainability in Africa. They are in North Africa, helping them deal with regional security well.
They take part in efforts to make the economy and governance better across Africa. This helps their countries and the African Union’s goals too.

These countries help improve relations across Africa. They join in many projects to help economic growth and better governance. This boosts their own interests and the African Union’s aims.
They are important in keeping peace and security in the region. They also help with projects that are good for the economy and society. This helps the whole continent.
| Country | Initiatives |
|---|---|
| Egypt | Peacekeeping missions, socio-economic development projects, regional security collaborations |
| Tunisia | Economic empowerment programmes, diplomatic relations enhancement, sustainable development campaigns |
Egypt and Tunisia are great examples of working together for Africa. They show how important they are to Africa’s peaceful, wealthy, and united future.
The Influence of the Mediterranean Sea
The influence of the Mediterranean Sea has shaped Egypt and Tunisia a lot. These countries have used the sea to make sea trade routes. These routes help them connect with the world. Their place by the sea helped in trade and made them cultural crossroads.
The Mediterranean influence has greatly helped their economies. History shows they had big trade networks. These networks brought goods, ideas, and new methods from places like Greece and Italy. This exchange made their cultures and societies richer, helping in arts, sciences, and how they are governed.
Egypt and Tunisia have used their geographic advantage well. They became bridges between Africa, the Middle East, and Europe. So they became more worldly. This made them see themselves as part of a bigger world.
| Egypt | Tunisia | |
|---|---|---|
| Historical Trade Routes | Yes | Yes |
| Influences from Europe | Extensive | Significant |
| Maritime Cultural Exchanges | Frequent | Frequent |
Is Tunisia In Egypt?
To clear up ‘Is Tunisia in Egypt?’, let’s look at common geographical misconceptions. Tunisia is its own country, not part of Egypt. Though both are in Africa, they are separate. They have their own land, leaders, and cultures.
They’re often mixed up because they’re close and share history. But, they are different countries. Knowing this helps clear up geographical misconceptions. It shows the value of their unique qualities in North Africa.
To make it simpler:
- Tunisia is next to Algeria and Libya.
- Egypt has Libya, Sudan, Israel, and Gaza Strip as neighbours.
- They have different capitals: Tunis for Tunisia and Cairo for Egypt.
These facts clear up any geographical misconceptions between Tunisia and Egypt. They show how both countries are unique but connected in North Africa.
FAQs About Tunisia and Egypt
Tunisia and Egypt have a long-shared history. Their bond is important in many ways. They have cultural ties and have been in the same empires. They work together in global groups and share business interests.
What connects Tunisia and Egypt?
Both countries are in North Africa. They have a lot in common. They are in groups like the African Union and the Arab League. This means they help each other in world matters.
They have been ruled by the same powers in the past. This history has brought them closer. They both work for peace in the Arab world.
How far apart are Egypt and Tunisia?
Egypt and Tunisia are far apart but still close in spirit. They sit each side of Libya, about 2,000 kilometers apart by air. The road distance is even longer. This shows they are geographically unique.
Yet, they share a regional identity. Their history keeps them connected. Knowing their distance shows both their closeness and individuality in North Africa.
Conclusion
Tunisia and Egypt have a lot in common. They both have rich histories and cultures. This makes them close in the North African region. However, they are different too. They are both independent countries with their own special stories. This shows that Tunisia is not part of Egypt. It highlights their importance in Africa.
These countries work together well. They have a history of working side by side. This includes old trading routes and the recent Arab Spring. They try hard to keep their region stable. They also work on growing their economies and keeping their cultures alive. This helps North Africa and beyond.
Lastly, Tunisia and Egypt show us how history can lead to teamwork. They share common goals because of their past. Yet, they are still unique. This helps them make North Africa stronger. They play a big role in their continent and the world.