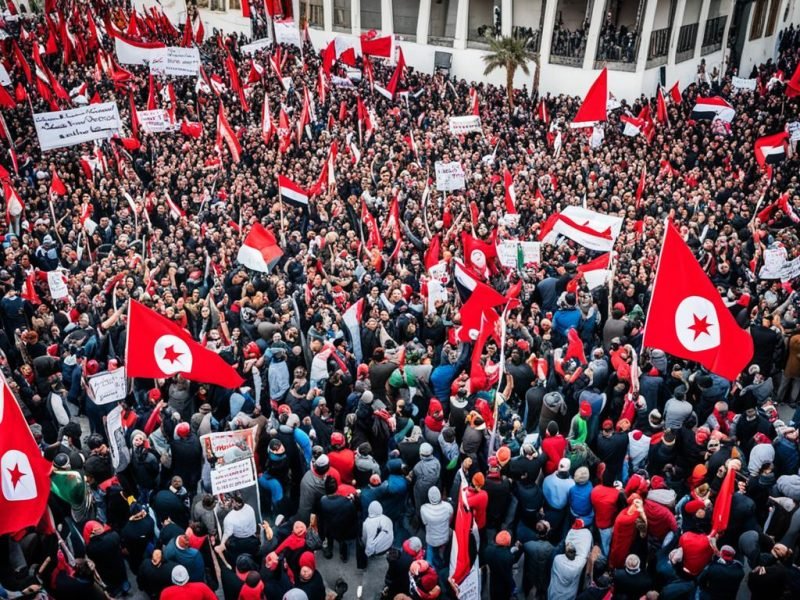
Did you know that three long-time leaders were removed in just 30 months? This happened during the Arab Spring. The Jasmine Revolution in Tunisia, the 2011 Egypt Uprising, and the 2011 Libya Revolt were key. They were big moments in the Middle East and North Africa.
Many people in North Africa were unhappy with their lives. They didn’t like the government’s control and wanted democracy. These feelings led to big changes. From Tunisia’s tragic event to Egypt and Libya’s leaders falling, the area changed a lot.
Key Takeaways:
- The Arab Spring began in Tunisia and sparked widespread uprisings across North Africa.
- Mohamed Bouazizi’s self-immolation in Tunisia was a major catalyst for the Jasmine Revolution.
- Egypt’s Tahrir Square protests led to the departure of President Hosni Mubarak.
- Libya’s violent uprising resulted in the killing of Muammar Gaddafi.
- Common grievances included political repression, economic hardships, and demands for democracy.
The Arab Spring: Introduction and Early Stages
The Arab Spring was a major event in North Africa. It started because of many reasons. Things like no jobs, poor economy, and unfair governments caused big problems.
What Triggered the Protests?
The Arab Spring began for several reasons. Mohamed Bouazizi’s self-immolation in Tunisia was a key moment. This sad act was a protest against poor living conditions and unfair treatment.
The energy crisis in the 2000s also made things worse. It led to more anger among the people.
Initial Responses from Governments
In North Africa, governments first responded harshly. Tunisia’s President tried to stop protests with violence and promises. But people stayed strong.
In Egypt and Libya, leaders did the same. They tried to stop the protests or make small changes. Yet, the protests led to big changes in politics.
Key Events of the Jasmine Revolution in Tunisia
The Jasmine Revolution was a key moment for Tunisia and the wider Arab Spring. It brought big political changes to Tunisia. The revolution started with a tragic event but led to big changes in politics.
Mohamed Bouazizi’s Self-Immolation
In December 2010, Mohamed Bouazizi, a street vendor, set himself on fire. He did this because he was upset with the police and corruption. His act started huge protests across the country. These protests were a big part of the Jasmine Revolution.
Overthrow of President Zine El Abidine Ben Ali
People in Tunisia were very angry. They held many protests. These protests made President Ben Ali leave the country on January 14, 2011. His leaving was a big deal. It showed people they could change a government.
Political Reforms and Elections
After Ben Ali left, Tunisia began to change its politics. A new government came in to help. In October 2011, there was a big vote. This vote started a new, democratic government. Tunisia showed it wanted democracy and change.
The January 25 Revolution in Egypt: A Timeline
The January 25 Revolution in Egypt showed real bravery and determination. People used social media to boost the revolution. This change came fast through sites that helped people protest against the regime.
Social Media and Organisation of Protests
Social media was key during the Egyptian revolution. Facebook and Twitter helped organize protests. They spread news fast. People planned big meetings at Tahrir Square using social media. The online world pushed people to act together in the real world.
Role of the Egyptian Military
The Egyptian military played a big role. They chose not to fight the protestors. This move got attention worldwide and support from locals. It showed the military supporting the people, not the rulers. The military then stopped backing President Hosni Mubarak. This helped the protestors win.
Departure of President Hosni Mubarak
The protests peaked on February 11, 2011. That’s when President Hosni Mubarak stepped down. He had been in charge for nearly 30 years. His leaving was a big win for the protestors. It marked the start of a new era, led by the military.
Libya’s Violent Revolt Against Muammar Gaddafi
Libya joined the Arab Spring with its uprising against Muammar Gaddafi. This uprising turned into an armed fight, unlike in Tunisia and Egypt.
The Escalation into Civil War
Libya’s protests soon became a fierce battle. The government’s violent response pushed people to fight back. This marked the start of the Civil War. Many groups joined in, making it more complex and deadly.
NATO Intervention
NATO played a huge role in fighting Gaddafi’s forces. They launched Operation Unified Protector to protect people. Their efforts weakened Gaddafi’s control, helping rebels move forward.
The Death of Muammar Gaddafi
Gaddafi’s rule ended in October 2011. Rebels found him in Sirte and his death ended his long rule. His fall was a big moment but led to more chaos.
Common Causes Across Tunisia, Egypt, and Libya
The Arab Spring involved many countries like Tunisia, Egypt, and Libya. They all faced similar big problems. These problems were mainly a bad economy and people wanting big political changes.
Economic Discontent
One big reason for the Arab Spring was economic troubles. Many people didn’t have jobs, were poor, and prices kept going up. This made people very upset. For example, Egypt had lots of young people without jobs. Tunisia saw prices go up fast and more people become poor. This made people want to change things.
Human Rights Violations
Bad treatment by the government also made people protest. In Tunisia, Egypt, and Libya, governments didn’t treat people well. They didn’t let people speak freely or gather together. When the government was too harsh, it made people even more determined to demand change.
Demands for Democracy
People in Tunisia, Egypt, and Libya all wanted democracy. They wanted to vote in fair elections and have more freedom. They were tired of corruption and leaders who were unfair. This hope for democracy brought many people together.
| Country | Economic Grievances | Human Rights Violations | Demands for Democracy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tunisia | High unemployment, poverty, inflation | Suppression of dissent, limited freedoms | Desire for free elections and civil liberties |
| Egypt | Youth unemployment, poverty, inflation | Authoritarian rule, human rights abuses | Call for political reform and democratic governance |
| Libya | Economic mismanagement, poverty | Repressive regime, lack of freedoms | End to corruption and demand for democracy |
North African Uprisings: Methods and Strategies
Protesters in North Africa used different ways to challenge regimes. They combined peaceful protests and digital campaigns. This mix helped to mobilise people and get global attention.
Civil Disobedience and Strikes
In places like Tunisia, protesters chose civil disobedience and strikes. They didn’t follow unfair laws and stopped working. Their goal was to make authorities listen to their demands. This showed the power of people standing together peacefully.
Internet and Media Activism
Social media played a big role in the uprisings. Platforms like Facebook and Twitter spread information fast. They helped to share what was happening, bring people together, and plan protests. The internet became a place to share the true story of the protests.
Protest Camps and Demonstrations
Protest camps and public demonstrations were key. Taking over public spaces showed they opposed the regimes. These camps were where activists planned together and supported each other. Sometimes, peaceful protests turned into violent ones when the authorities tried to stop them.
What Happened In Tunisia, Egypt, And Libya?
The Summary of Arab Spring shows different stories in Tunisia, Egypt, and Libya. In Tunisia, Mohamed Bouazizi set himself on fire. This act set off big protests. These protests made President Zine El Abidine Ben Ali leave.
Tunisia then changed its government. This was a first in the area. It led to political change and free elections.
In Egypt, the story was different. Social media helped to get many people to protest. These protests and the army’s role pushed President Hosni Mubarak to resign. But, after that, Egypt faced hard times.
It wasn’t easy to find stability.
Libya’s story is more violent. The Armed uprisings turned into a big war. The world paid a lot of attention. NATO even got involved.
This led to Muammar Gaddafi’s death. But, Libya has been in trouble since. It’s still fighting.
Each country kicked out its ruler. But each country had its own way of doing it. They all faced big challenges afterwards. These stories show how the Arab Spring changed things, but not always as expected.
| Country | Key Event | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Tunisia | Bouazizi’s Self-Immolation | Overthrow of Ben Ali, Democratic Reforms |
| Egypt | Mass Protests, Military Involvement | Resignation of Mubarak, Political Uncertainty |
| Libya | Civil War, NATO Intervention | Death of Gaddafi, Ongoing Conflict |
This Summary of Arab Spring shows how Tunisia, Egypt, and Libya each took a different path. It shows the complex ways countries can change their leaders during political troubles.
International Reactions to the Arab Spring
Countries around the world reacted differently to the Arab Spring. Their responses depended on their own interests and alliances. While some nations backed the uprisings, others worried about the effects on the wider area.
Role of Foreign Interventions
Many countries got involved in the Arab Spring. For example, NATO’s actions in Libya helped to end Muammar Gaddafi’s rule. These actions showed their own interests but also cared about humanitarian needs and the region’s future.
UN and NATO Involvement
The UN and NATO were key players, especially in Libya. The UN allowed military actions to save civilians. This had big effects on international relationships and the situation in the region. NATO used airstrikes and set up no-fly zones, showing how complex responses from around the world were.
Reactions from Neighbouring Countries
Countries next to those in the Arab Spring had varied reactions. Qatar, for instance, supported the protests with resources and diplomacy. Saudi Arabia, however, was worried. They feared similar protests could start within their own borders. They also were concerned about the area’s stability.
Impact of the Arab Spring on Regional Politics
The political aftermath of the Arab Spring changed power in North Africa and the Middle East. It led to democratic changes and big power fights.
Shift Towards Democracy
Early stages of the Arab Spring saw countries like Tunisia move towards democratic transitions. Dictators were overthrown, and new elections happened. This time saw more political activity and new parties aiming for democracy.
Power Struggles and Power Vacuums
Yet, not every country had an easy time moving to democracy. Take Libya, for instance. The fall of Muammar Gaddafi led to a long civil war. The fight for power became difficult, making stability hard to achieve. This showed the complex effects of the Arab Spring on the region.
| Country | Outcome | Current Status |
|---|---|---|
| Tunisia | Democratic Transition | Stable with Challenges |
| Egypt | Military Influence | Authoritarianism |
| Libya | Civil War | Ongoing Conflict |
Long-Term Consequences for Tunisia
Tunisia has been on a complex path since the Arab Spring. It has seen big political changes. These changes have helped shape the country after the revolution.
Political Reforms and Stability
At the heart of Tunisia’s new era are political reforms. In 2014, the country got a new constitution. This was a big step towards democracy, leading to free elections.
The constitution gave people more freedoms. It set up a system to keep the government in check. This system promotes human rights and includes everyone in governance. Yet, keeping the country stable is an ongoing task.
Economic Conditions Post-Revolution
Political progress has been made, but economic challenges remain. The revolution’s after-effects have slowed down economic recovery. Joblessness is high, especially among young people. This is a big issue for growth.
The government is working to make things better. They want to attract more investment and tourists. They are also trying to help private businesses grow. A strong economy is crucial for Tunisia’s future.
- Political reforms include a new constitution, free elections, and civil liberties improvements.
- Challenges in economic recovery such as unemployment and sustainable development remain.
- Continuous governmental initiatives strive to ensure political stability and economic growth.
| Focus Area | Achievements | Challenges |
|---|---|---|
| Political Reforms | New constitution, free elections, human rights advancements | Ensuring continuous political stability |
| Economic Conditions | Efforts for foreign investment and tourism revivals | High unemployment rates, sustainable growth |
Long-Term Consequences for Egypt
Egypt’s journey after the Arab Spring has been tough. Hopes for democracy have faded away. Now, authoritarian rule is shaping the scene.
Return of Authoritarianism
After the Arab Spring, Egypt saw a short time of democracy. But it didn’t last long. President Abdel Fattah el-Sisi’s rule has brought back strict control and little freedom.
Military Influence in Politics
The military in Egypt holds a lot of power. Its strong role has stopped real democracy from growing. With less civilian control, Egypt’s politics remain complicated.
Impact on Civil Society
Civil society groups in Egypt are under pressure. They find it hard to fight for rights and freedom. The government’s tight grip has made their work even tougher.
The revolution’s effects on Egypt are deep and long-lasting. It has changed the country’s social and political life a lot.
Long-Term Consequences for Libya
After Muammar Gaddafi fell, Libya faced hard times. The country has been in a civil war, with big problems for people. Governance is split up too, hurting society a lot.
Ongoing Civil War
With Gaddafi gone, Libya fell into war. Many groups are fighting for power. This war makes peace hard to achieve.
Humanitarian Crisis and Refugee Flows
The war caused big problems for civilians. Many had to leave their homes or even the country. With systems broken, lots need help with health, school, and basic needs.

Fragmented Governance
Libya’s government is all over the place. Many groups say they should be in charge. This makes fixing and ruling the country very tough.
| Key Issues | Impact |
|---|---|
| Ongoing Civil War | Continuous conflict and fragmented leadership |
| Humanitarian Crisis | Displacement, refugee flows, and infrastructure breakdown |
| Fragmented Governance | Multiple competing authorities, lack of central control |
Fixing Libya after Gaddafi is complex. The world must work together long-term. Only then can peace and stability return.
Conclusion
The Arab Spring deeply changed North Africa and the Middle East. Looking back at Tunisia, Egypt, and Libya, we see a mix of big changes and ongoing fights. These uprisings led to some moves toward democracy, like political changes in Tunisia and Egypt’s elections.
But, finding stable democracy has been hard. Libya fell into a long civil war. This shows the hard issues that come up when dictators are overthrown. Thinking about the Middle East’s future, we see that people still deeply want freedom and to choose their own path. This hope stays strong, despite problems.
We also need the world to help and support these changes, to help bring good results out of the chaos. Looking at the Arab Spring, we learn why it’s important to keep watching and working together. The lessons from the Arab Spring show us the hope for a better future is still here.







